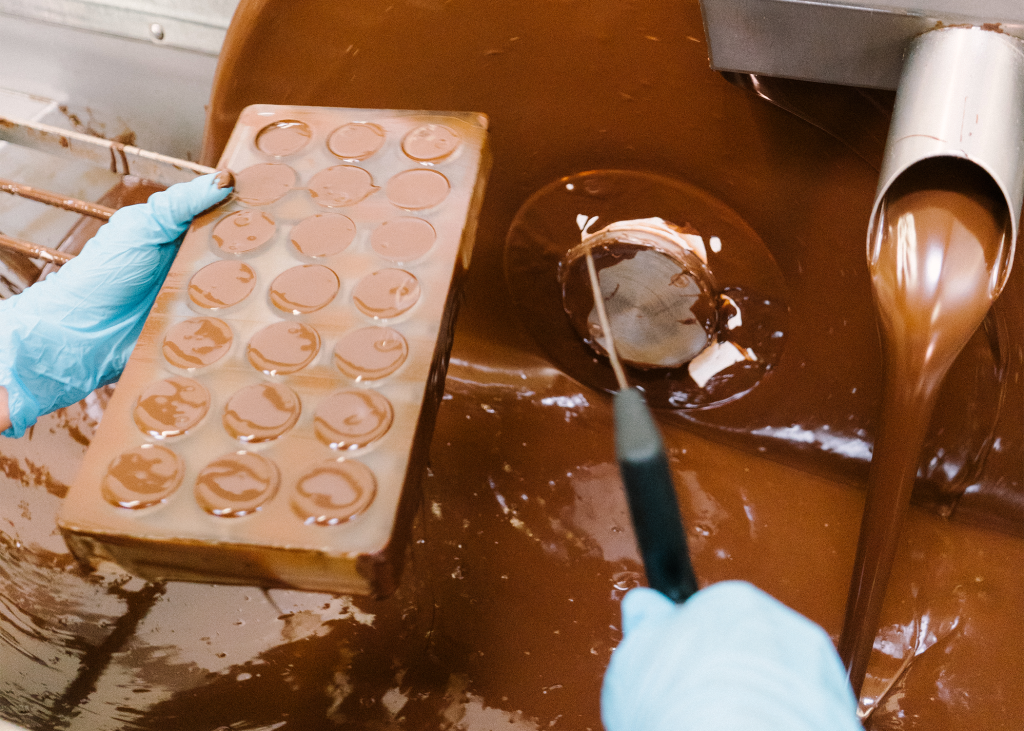

When it comes to food, quality starts with what’s inside. As a company built around keeping food clean, we encourage our customers to learn about and even question what’s on the label.
We know that great taste doesn’t need to be complicated, which is why we use simple, high-quality, organic ingredients to allow the chocolate to speak for itself. We enjoy exploring how organic cocoa, cocoa butter, varieties of nuts, fruits and other delightful flavors found in nature can create a superior product without the need for artificial ingredients. There’s one ingredient that’s a little less familiar that we’d like to talk about. Meet sunflower lecithin.
What in the world is lecithin?
Lecithin is a group of fats naturally present in all living plant and animal tissues. It is an amphiphilic compound, which means it attracts both water and fatty substances. Without lecithin and other membrane phospholipids, cells would be unable to maintain their structure and probably would dissolve back into their surroundings. Studies have shown that lecithin reduces cholesterol, improves brain health and supports immune function. Some cosmetic products even include lecithin as a skin moisturizing component.
What is it doing in my food?
A handful of foods are already naturally high in lecithin. Egg yolks, soybeans, whole grains, milk, peanuts, wheat germ and organ meats have higher concentrations. And because of its ability to bind two liquids that do not typically mix well together, lecithin is a common emulsifier in commercial foods. Its chemical properties have both water loving (hydrophilic) and oil loving (hydrophobic) regions, allowing things like water and oil to join. And that’s where we come in.
Why is lecithin used in chocolate?
In chocolate, lecithin is the matchmaker between cocoa butter and dry solids (sugar) and the reason behind chocolate’s shiny, uniformly distributed, melt in your mouth consistency. Without lecithin, these ingredients tend to separate, leaving a light oily film on the surface. In addition to being an excellent binding agent, lecithin lowers the viscosity of chocolate, making it easier to temper (the process of giving chocolate its smooth mouthfeel and shine). This is especially important for achieving that delicate, thin chocolate shell on our organic and vegan chocolate truffles and assortments. Finally, lecithin stabilizes oils against oxidation, slowing down chocolate bloom and extending the shelf life.
“In chocolate, lecithin is the matchmaker between cocoa butter and dry solids (sugar) and the reason behind chocolate’s shiny, uniformly distributed, melt in your mouth consistency.”

Anything else I need to know?
Yes! Where you derive your lecithin matters. Lecithin can be extracted from egg yolk, sunflower, soybeans, milk, fish, animal fat, canola seeds, and cotton seeds. As a vegan company that keeps its facilities free from soy, we use sunflower lecithin in our chocolates.
Sunflower lecithin is superior in health benefits as it contains a higher level of phospholipid choline (which is linked to better metabolism, cell growth, DNA synthesis, and nervous system function) and is not genetically modified. Soy lecithin, the most common form of the commercial lecithin, is derived from soybeans. Its extraction involves chemicals such as acetone and hexane whereas sunflower lecithin extraction happens via cold pressing without the use of any chemical.
All that said, lecithin makes up less than .0004% of our chocolate. But to hold our end of the bargain of keeping food clean – every ingredient is thoughtfully considered before making it into a bite, bar or boxed assortment.

Comments
Add a Comment
There are no comment yet.